Linux内核源码走读之IPv4及IPv6
最近在看内核网络协议栈的代码,打算写几篇文章记录下。本文是关于IPv4及IPv6相关的内核源码走读,包括IPv4/IPv6的初始化,以及IP报文的接收和发送。
IPv4
IPv4报头
首先看下IPv4报头的定义,对应内核源码中的结构体是struct iphdr:
struct iphdr {
__u8 ihl:4, //header length, 以4字节为单位,最小为4,最大为15
version:4; //总是4
__u8 tos;
__be16 tot_len; //包括报头在内的数据包总长度
__be16 id; //对于分段来说,所有分段的id值都必须相同
__be16 frag_off; //后13bit为分段的偏移量,以8Byte为单位
__u8 ttl; //存活时间,每个转发节点都会将ttl减1
__u8 protocol; //包所属的第四层协议
__sum16 check; //报头校验和
__be32 saddr; //源IP地址
__be32 daddr; //目的IP地址
/*The options start here. */ //IP选项,可选
};
IPv4的初始化
//net/ipv4/af_inet.c
static int inet_init(void)
proto_register(&tcp_prot, 1) //所有注册的协议可以通过cat /proc/net/protocols查看
proto_register(&udp_prot, 1)
proto_register(&raw_prot, 1)
proto_register(&ping_prot, 1)
sock_register(&inet_family_ops)
//注册各协议的接收处理函数,最终赋值到全局变量inet_protos[protocol]
inet_add_protocol(&icmp_protocol, IPPROTO_ICMP)
inet_add_protocol(&udp_protocol, IPPROTO_UDP)
inet_add_protocol(&tcp_protocol, IPPROTO_TCP)
inet_add_protocol(&igmp_protocol, IPPROTO_IGMP)
//注册各协议的socket interface接口
for (q = inetsw_array; q < &inetsw_array[INETSW_ARRAY_LEN]; ++q)
inet_register_protosw(q);
arp_init() //arp模块初始化
dev_add_pack(&arp_packet_type) //注册ETH_P_ARP=0x0806类型的处理函数
arp_proc_init() //cat /proc/net/arp, 查看arp表项
register_netdevice_notifier(&arp_netdev_notifier) //注册netdevice事件监听
ip_init()
ip_rt_init //ip路由相关的初始化
devinet_init
//注册netdevice时间回调
register_netdevice_notifier(&ip_netdev_notifier);
//这里ip_netdev_notifier的回调函数是inetdev_event,看下这个回调
int inetdev_event(struct notifier_block *this, unsigned long event,void *ptr)
if (event == NETDEV_REGISTER)
//给net_device创建in_device,in_device即ip相关的配置,比如ip地址
//可以通过ip或ifconfig来修改
in_dev = inetdev_init(dev);
tcp_init()
udp_init()
ping_init()
icmp_init()
icmp_sk_init(struct net *net)
//每CPU注册一个ICMP RAW socket,用于处理接收的ICMP报文
inet_ctl_sock_create
ip_mr_init //组播路由初始化
//注册IP协议ETH_P_IP=0x0800接受处理函数ip_rcv,即注册IP报文接收入口函数
dev_add_pack(&ip_packet_type)
这里展开看一下dev_add_pack函数
void dev_add_pack(struct packet_type *pt)
struct list_head *head = ptype_head(pt)
return &ptype_base[ntohs(pt->type)] //ptype_base是一个全局变量数组,记录每个协议的处理函数
list_add_rcu(&pt->list, head) //将处理函数pt赋值到全局变量ptype_base中
接收IPv4数据包
Linux网卡驱动接收包有两种方式,NAPI和非NAPI。现在新的网卡驱动一般采用NAPI方式。 网卡驱动在通过接收中断、软中断等一些列处理后,最终调用napi_gro_receive将数据包上报到协议栈处理。
非NAPI方式,最终调用netif_rx。这里跟一下从napi_gro_receive开始的收包流程。
gro_result_t napi_gro_receive(struct napi_struct *napi, struct sk_buff *skb)
napi_skb_finish(dev_gro_receive(napi, skb), skb);
netif_receive_skb_internal
__netif_receive_skb
__netif_receive_skb_core
__netif_receive_skb_core可以认为是内核协议栈处理接收包的起点,下面跟一下这个函数。
static int __netif_receive_skb_core(struct sk_buff *skb, bool pfmemalloc)
//ptype_all是所有包类型的接收处理,对应tcpdump、raw socket等处理
list_for_each_entry_rcu(ptype, &ptype_all, list)
if (pt_prev)
ret = deliver_skb(skb, pt_prev, orig_dev);
pt_prev = ptype;
//如果这个设备有注册rx_handler,通过接口netdev_rx_handler_register注册
//则将包交给注册的rx_handler处理。例如加入网桥的接口会被注册rx_handler
rx_handler = rcu_dereference(skb->dev->rx_handler);
if (rx_handler)
rx_handler(&skb)
//交给ptype_base里注册的对应协议类型的处理函数
deliver_ptype_list_skb(skb, &pt_prev, orig_dev, type,
&ptype_base[ntohs(type) & PTYPE_HASH_MASK]);
ptype_base里的对象是通过dev_add_pack接口注册的,在上节IPv4初始化里,我们知道IPv4协议注册的对象是ip_packet_type
static struct packet_type ip_packet_type __read_mostly = {
.type = cpu_to_be16(ETH_P_IP),
.func = ip_rcv, //IP协议报文的入口
};
接下来跟踪ip_rcv源码。
int ip_rcv(struct sk_buff *skb, struct net_device *dev, struct packet_type *pt, struct net_device *orig_dev)
iph = ip_hdr(skb);
if (iph->ihl < 5 || iph->version != 4) //如果包长度小于20或版本不是4,则报头不合法
goto inhdr_error;
if (unlikely(ip_fast_csum((u8 *)iph, iph->ihl))) //报头校验和校验
goto csum_error;
//netfilter的第一个钩子挂载点,NF_INET_PRE_ROUTING
//如果没被netfilter过滤,最终调用ip_rcv_finish
return NF_HOOK(NFPROTO_IPV4, NF_INET_PRE_ROUTING,
net, NULL, skb, dev, NULL,
ip_rcv_finish);
static int ip_rcv_finish(struct net *net, struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb)
if (!skb_valid_dst(skb))
//在路由选择子系统进行查找
err = ip_route_input_noref(skb, iph->daddr, iph->saddr,iph->tos, dev);
//ip_route_input_noref中如果判断此IP包是发给本地,
//则skb->_skb_refdst的input函数赋值为ip_local_deliver
//如果需要转发,则iput函数赋值为ip_forward
if (iph->ihl > 5 && ip_rcv_options(skb, dev)) //ip报头的选项处理
goto drop;
//调用路由选择子系统查找到的input函数
return dst_input(skb);
skb_dst(skb)->input(skb) //即调用skb->_skb_refdst对象的input函数
//这里看一下struct dst_entry,即路由查找的结果
struct dst_entry {
...
int (*input)(struct sk_buff *); //路由查找后的接收处理函数,发给本机的包对应函数为ip_local_deliver
int (*output)(struct net *net, struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb);
...
}
继续看一下IP包发给本地时的处理函数ip_local_deliver
int ip_local_deliver(struct sk_buff *skb)
if (ip_is_fragment(ip_hdr(skb)))
ip_defrag //如果是分片报文,则交给解分片函数处理
//netfilter的第二个钩子挂载点NF_INET_LOCAL_IN
return NF_HOOK(NFPROTO_IPV4, NF_INET_LOCAL_IN,
net, NULL, skb, skb->dev, NULL,
ip_local_deliver_finish);
static int ip_local_deliver_finish(struct net *net, struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb)
//先查并发给raw socket
raw = raw_local_deliver(skb, protocol);
ipprot = rcu_dereference(inet_protos[protocol]); //inet_protos: 各协议注册的处理函数
if (ipprot)
ret = ipprot->handler(skb); //调用注册的协议处理函数,通过接口inet_add_protocol注册
//比如IPPROTO_ICMP的处理函数icmp_rcv,IPPROTO_TCP的是tcp_v4_rcv
发送IPv4数据包
IPv4为L4层提供将数据包发到L2层的接口和功能。
从L4发送IPv4数据包的主要方法有两个,一个是方法ip_queue_xmit(),由TCPv4使用;一个是ip_append_data(),由UDPv4和ICMPv4使用。
先看方法ip_queue_xmit()
int ip_queue_xmit(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb, struct flowi *fl)
struct rtable *rt;
//在路由子系统中查找路由
rt = ip_route_output_ports
ip_route_output_flow
__ip_route_output_key
ip_route_output_key_hash
ip_route_output_key_hash_rcu(net, fl4, &res, skb);
fib_lookup(net, fl4, res, 0);
skb_dst_set_noref(skb, &rt->dst);
... //此处是一些填写ip header的逻辑
res = ip_local_out(net, sk, skb);
__ip_local_out
//netfilter钩子挂载点NF_INET_LOCAL_OUT
nf_hook(NFPROTO_IPV4, NF_INET_LOCAL_OUT,
net, sk, skb, NULL, skb_dst(skb)->dev,
dst_output);
dst_output(net, sk, skb)
skb_dst(skb)->output(net, sk, skb) //一般地,这里的output是ip_output
//继续看下ip_output
int ip_output(struct net *net, struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb)
//netfilter的钩子挂载点NF_INET_POST_ROUTING
NF_HOOK_COND(NFPROTO_IPV4, NF_INET_POST_ROUTING,
net, sk, skb, NULL, dev,
ip_finish_output,
!(IPCB(skb)->flags & IPSKB_REROUTED));
//ip_finish_output
static int ip_finish_output(struct net *net, struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb)
ip_finish_output2
//从字面上理解,找到目的邻居,然后发给邻居
neigh = __ipv4_neigh_lookup_noref(dev, nexthop);
res = neigh_output(neigh, skb);
dev_queue_xmit //最终交给网卡驱动
再看方法ip_append_data
int ip_append_data(struct sock *sk, struct flowi4 *fl4,
int getfrag(void *from, char *to, int offset, int len,
int odd, struct sk_buff *skb),
void *from, int length, int transhdrlen,
struct ipcm_cookie *ipc, struct rtable **rtp,
unsigned int flags)
__ip_append_data
//此函数很长,此处略过。
转发
在前面接收IPv4数据包中讲到,接收的数据包经过路由查找后,如果是发给本机的,则走到ip_local_deliver。 如果是要转发,则走到ip_forward。下面看下ip_forward的代码。
int ip_forward(struct sk_buff *skb)
//netfilter挂载点 NF_NET_FORWARD
return NF_HOOK(NFPROTO_IPV4, NF_INET_FORWARD,
net, NULL, skb, skb->dev, rt->dst.dev,
ip_forward_finish);
static int ip_forward_finish(struct net *net, struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb)
dst_output(net, sk, skb)
//dst_output在上节讲到过,最终会调用到dev_queue_xmit交给网卡驱动
关于IPv4,还有一些主题,比如接收组播数据包、IP选项、分段等,后面有时间再补充。
IPv4报文接收和发送的流程图如下:
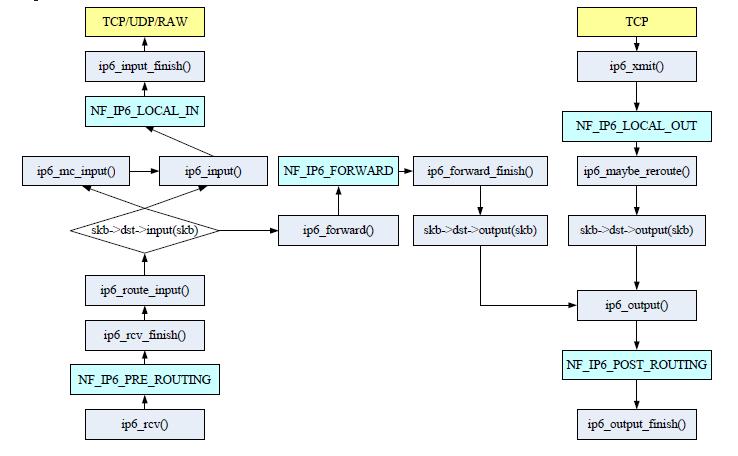
IPv6
IPv6地址
学习IPv6之前,先看下IPv6地址。IPv6地址长度为128bit,由8部分组成,每部分16bit。
IPv6地址的写法为: xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx。
如果一部分、或连续的几部分都为0,则可用::表示。
在IPv6中,需要用到地址前缀,前缀相当于IPv4子网掩码,用/n表示。 比如2001:da7::/32,表示开头32bit为2001:0da7的所有IPv6地址。
一些特殊的IPv6地址:
- 每个接口都必须至少有一个链路本地单播地址。路由器不得转发此地址的包。地址前缀为fe80::/64
- 全局单播地址的通用格式如下:n位全局路由选择前缀,m位子网ID,余下的为接口ID
- ::1为环回地址
- 全0(0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0)地址称为未指定地址,用于DAD(重复地址检测)
- 映射IPv4的IPv6地址,前80位为0,接下来16位为1,余下32位为IPv4地址,例如:::ffff:192.0.2.128
在Linux中,IPv6地址用in6_addr表示。
struct in6_addr {
union {
__u8 u6_addr8[16]; //用union定义了3种形式的128bit长度
__be16 u6_addr16[8];
__be32 u6_addr32[4];
} in6_u;
#define s6_addr in6_u.u6_addr8
#define s6_addr16 in6_u.u6_addr16
#define s6_addr32 in6_u.u6_addr32
};
IPv6报头
IPv6报头在Linux中的结构体是struct ipv6hdr:
struct ipv6hdr {
__u8 priority:4, //流量优先级
version:4; //版本号,总是6
__u8 flow_lbl[3]; //流标签
__be16 payload_len; //数据包的长度,不包含包头
__u8 nexthdr; //扩展报头或者上层协议编号
__u8 hop_limit; //相当于ttl
struct in6_addr saddr; //128bit源地址
struct in6_addr daddr; //128bit目的地址
};
IPv6扩展报头: IPv6报头的nexthdr字段,指出下一个报头的编号。没有扩展报头或最后一个扩展报头,指示上层协议。
IPv6初始化
inet6_init执行各种IPv6的初始化工作,位于net/ipv6/af_inet6.c
static int __init inet6_init(void)
//和IPv4初始化类似,一堆协议注册。没跟到这里注册的协议后面怎么用。
proto_register(&tcpv6_prot, 1)
proto_register(&udpv6_prot, 1)
proto_register(&udplitev6_prot, 1)
proto_register(&rawv6_prot, 1)
proto_register(&pingv6_prot, 1)
rawv6_init()
sock_register(&inet6_family_ops)
inet6_net_init
ip6_mr_init
icmpv6_init
icmpv6_sk_init
//注册ICMPv6的接收处理函数icmpv6_rcv
inet6_add_protocol(&icmpv6_protocol, IPPROTO_ICMPV6)
ndisc_init()
igmp6_init
ipv6_netfilter_init
ip6_route_init
ipv6_frag_init
inet6_add_protocol(&frag_protocol, IPPROTO_FRAGMENT)
udpv6_init
inet6_add_protocol(&udpv6_protocol, IPPROTO_UDP)
tcpv6_init
inet6_add_protocol(&tcpv6_protocol, IPPROTO_TCP)
ipv6_packet_init()
//注册IPv6协议的接收处理函数 ipv6_rcv
//ETH_P_IPV6 = 0x86DD
dev_add_pack(&ipv6_packet_type);
接收IPv6数据包
IPv6数据包的主接收方法为ipv6_rcv(),看下这个函数源码
int ipv6_rcv(struct sk_buff *skb, struct net_device *dev, struct packet_type *pt, struct net_device *orig_dev)
... //此处省略一系列校验和检查
//netfilter挂载点NF_INET_PRE_ROUTING,最终调用ip6_rcv_finish
return NF_HOOK(NFPROTO_IPV6, NF_INET_PRE_ROUTING,
net, NULL, skb, dev, NULL,
ip6_rcv_finish);
int ip6_rcv_finish(struct net *net, struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb)
//路由查找
ip6_route_input(skb);
ip6_route_input_lookup
fib6_rule_lookup
return dst_input(skb);
skb_dst(skb)->input(skb); //调用路由查找后的input函数
//如果是给当前主机的包input为ip6_input
//如果需要转发input为ip6_forward
//如果数据包目的地址为组播input为ip6_mc_input
这里看下本地投递的情形,此时skb_dst(skb)->input函数为ip6_input
int ip6_input(struct sk_buff *skb)
//netfilter挂载点NF_INET_LOCAL_IN
return NF_HOOK(NFPROTO_IPV6, NF_INET_LOCAL_IN,
dev_net(skb->dev), NULL, skb, skb->dev, NULL,
ip6_input_finish);
static int ip6_input_finish(struct net *net, struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb)
raw6_local_deliver //先投递给原始套接字
ipprot = rcu_dereference(inet6_protos[nexthdr])
if (ipprot)
ipprot->handler(skb) //调用在IPv6初始化时注册的协议处理函数
发送IPv6数据包
IPv6数据包的发送路径与IPv4很像。IPv6中也有两个发送IPv6数据包的主方法: 一个是ip6_xmit,由TCP、SCTP等使用;另一个是ip6_append_data,有UDP和RAW套接字使用。
最终的调用路径为:ip6_local_out->ip6_output->ip6_finish_output->交给网卡驱动。
IPv6报文接收和发送的流程图如下: